Why Kubernetes is important for the future of data platforms?
Introduction #
In brief, Kubernetes is a platform for automating and allocating containers that includes built-in features for healing, scheduling, and deployment practices (such as rollouts and rollbacks), as well as load-balancing and auto-scaling capabilities. Containers are abstracted by the name “Pod” within Kubernetes.
Kubernetes architecture #
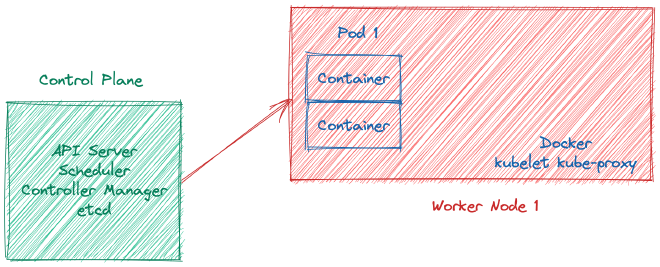
Problem #
Nowadays, numerous industries face the challenge of collecting and integrating data to solve complex problems. These data-centric problems span from customer service to process automation, and as the number of problems increases, so does the volume of data that needs to be processed. Consequently, the information technology industry is expected to deliver robust, reliable, and scalable data and machine learning solutions more than ever before, to meet the demands of the rapidly growing data volumes.
Proposed System #
Almost all data-intensive applications require either batch or real-time data processing. These applications include analytics reports, machine learning tasks, and real-time advertising campaign actions, all of which process large volumes of collected data.
For several years, Hadoop has been the preferred choice for batch data processing, and it has primarily used YARN for resource management. However, with the emergence of containerization, Mesos has become a popular resource manager for Hadoop environments. In contrast, real-time processing has always been more complex than batch processing and requires different concepts such as watermarks.
Data applications involve significant computation tasks that must handle large amounts of data at scale. Consequently, these applications require distributed systems and task orchestrations to manage computation devices, processes, threads, containers, pods, or other resources.
Schedulers are crucial for managing data workloads, whether it is a simple data processing job or a multi-component machine-learning operation flow. Machine learning models typically require an API server, while API servers require load balancing and other microservices concepts.
Finally, cloud flexibility is a critical consideration for data applications as they must be capable of running on different platforms such as private, public, or hybrid cloud. Data is a valuable asset for companies and governments, and as regulations increase, the importance of data management and processing is only likely to grow. The data race has just begun.
Conclusion #
Managing these types of problems and systems can be complex, but Kubernetes has emerged as a solution with several competitive advantages, including:
- Resource efficiency: Kubernetes optimizes the use of computing resources and ensures that containers are efficiently allocated to nodes.
- Seamless scalability on containers or nodes: Kubernetes allows for seamless scaling of containers or nodes based on the needs of the application.
- Built-in scheduler: Kubernetes has a built-in scheduler that automates the deployment and scaling of containers and manages the allocation of computing resources.
- Cloud flexibility: Kubernetes provides the flexibility to run applications on different cloud platforms, including private, public, and hybrid clouds.
- Pushing to apply engineering best practices: Kubernetes encourages the use of best practices in software engineering, such as containerization, microservices, and continuous integration and delivery, to improve the reliability and scalability of applications.